Tense Chart in English: Rules, Examples, and Types
Tense Chart Intro:
Welcome to our blog post on “Tense Chart in English: Rules, Examples, and its Types.” Understanding the various tenses in English is crucial for effective communication and writing. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different tenses found in the English language, and their rules, provide illustrative examples, and delve into their respective types. Whether you are a language learner looking to enhance your grammar skills or a writer aiming to improve your sentence structure, this blog post will serve as an invaluable resource. Get ready to unravel the complexities of English tenses as we break them down, provide clear explanations, and equip you with the knowledge to confidently navigate through various tenses. Let’s embark on this linguistic journey together and unlock the secrets of the English language!
What is Tense?
According to Oxford Dictionary, “Tense is any of the forms of a verb that may be used to show the time of the action or situation expressed by the verb”.
According to Merriam-Webster Dictionary, “The term tense means a distinction of form in a verb to express distinctions of time or duration of the action or state it denotes”.
According to Collins Dictionary, “Tense is defined as any of the forms of a verb which reveal the time at which an action has happened”.
According to Cambridge Dictionary defines “tense” as “any of the forms of a verb which show the time at which an action happened.”
Rules and Examples:
- Simple Present:
- Used for general truths or habits.
- Example: The sun rises in the east.
- Present Continuous:
- Used for ongoing actions in the present.
- Example: She is watching a movie right now.
- Present Perfect:
- Used to indicate past actions with present relevance.
- Example: I have visited Paris before.
- Present Perfect Continuous:
- Used to express the duration of an action that started in the past and continues to the present.
- Example: They have been studying all night.
- Simple Past:
- Used to talk about completed actions in the past.
- Example: He finished his work yesterday.
- Past Continuous:
- Used for actions that were in progress in the past.
- Example: We were having dinner when the phone rang.
- Past Perfect:
- Used to express an action that occurred before another action in the past.
- Example: She had already left when I arrived.
- Past Perfect Continuous:
- Used to indicate the duration of an action that started and continued before another action in the past.
- Example: I had been waiting for two hours when they finally arrived.
- Simple Future:
- Used to talk about actions that will happen in the future.
- Example: They will meet us at the restaurant tomorrow.
- Future Continuous:
- Used to express actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future.
- Example: I will be studying at this time tomorrow.
- Future Perfect:
- Used to show that an action will be completed before a specific time in the future.
- Example: By next month, I will have finished my project.
- Future Perfect Continuous:
- Used to express the duration of an action that will be ongoing before a specific time in the future.
- Example: By the time she arrives, I will have been waiting for three hours.
Types of Tense
In English Grammar, tenses are of three types, that is,
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
Further, it consists of four forms:
- Simple
- Perfect
- Continuous
- Perfect Continuous
So, in total there are 12 tenses which are as follows:
| Tenses | Tenses forms |
| Present Tense | Simple Present Tense |
| Present Perfect Tense | |
| Present Continuous Tense | |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Past Tense | Simple Past Tense |
| Past Perfect Tense | |
| Past Continuous Tense | |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | |
| Future Tense | Simple Future Tense |
| Future Perfect Tense | |
| Future Continuous Tense | |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense |
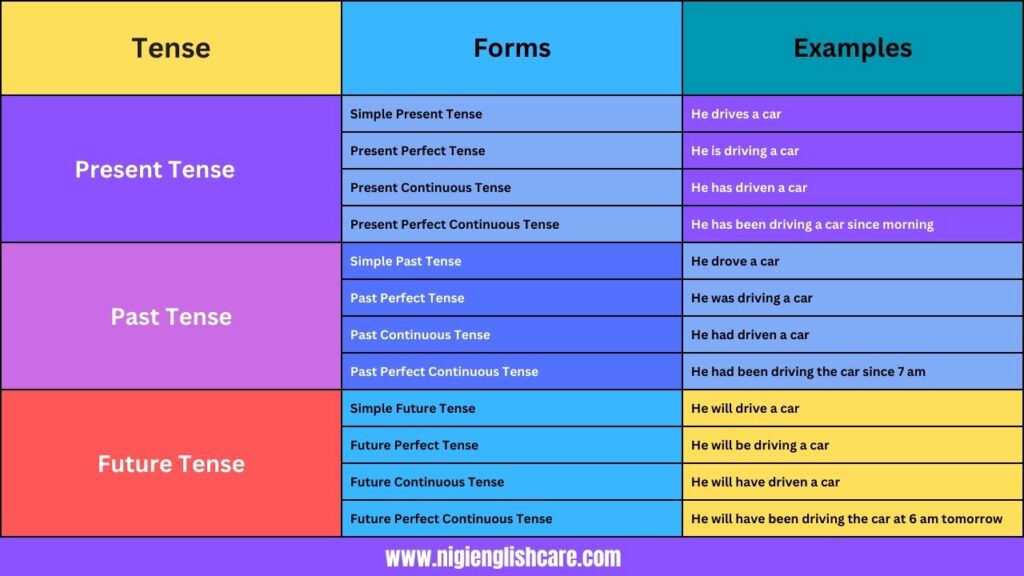
Below is the table of examples of tenses-
| Tense | Forms | Examples |
| Present Tense | Simple Present Tense | He drives a car |
| Present Perfect Tense | He is driving a car | |
| Present Continuous Tense | He has driven a car | |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | He has been driving a car since morning | |
| Past Tense | Simple Past Tense | He drove a car |
| Past Perfect Tense | He was driving a car | |
| Past Continuous Tense | He had driven a car | |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | He had been driving the car since 7 am | |
| Future Tense | Simple Future Tense | He will drive a car |
| Future Perfect Tense | He will be driving a car | |
| Future Continuous Tense | He will have driven a car | |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | He will have been driving the car at 6 am tomorrow |
Significance of Tense Chart
The English Grammar, tenses are often considered an important concept. A verb when changing its form takes the help of tense to formulate the proper sentence or express the state of action, events, or occurrence in a proper way. It helps you to make your context clear and precise. You may also create complex sentence constructions using tenses. Therefore, you should be familiar with all twelve tenses and their usage, so for that, we have made a tense chart below to make you understand better.
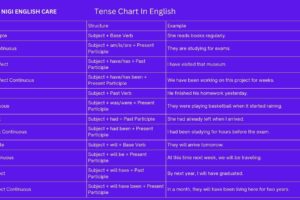
Tense Chart with Rules and Examples
| Tense Chart | ||
|---|---|---|
| Tenses | Rules and Formula | Examples |
| Simple Present Tense | Subject + Verb in the base form/third person plural form + the rest of the sentence | My sister eats bread and butter before going to school. |
| Present Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb(am/is/are) + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | Many people are going to NIGI English Care. |
| Present Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (have/has) + Past participle of the main verb + the rest of the sentence along with the time frame | She has lived here all her life with her husband. |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Have/Has + Been + Verb+ ing + the rest of the sentence | I have been working on this project for a week. |
| Simple Past Tense | Subject + Verb + ed / verb in the past tense + the rest of the sentence | My father went to Chennai yesterday. |
| Past Continuous Tense | Subject + Helping Verb(was/were) + Main verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | It was snowing today. |
| Past Perfect Tense | Subject + Helping Verb (had) + Past participle of the main verb + the rest of the sentence along with the time frame. | She had met him before the party. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + Had + Been + Verb + ing + the rest of the sentence | He had been drinking milk out the carton when Mom walked into the kitchen. |
| Simple Future Tense | Subject + will/shall + V1 + Object | I will write articles on different topics. |
| Future Continuous Tense | Subject + will be/shall be + V1 + ing + Object | I will have been waiting here for three hours by six o’clock. |
| Future Perfect Tense | Subject + will have/shall have + V3 + Object | I will have dressed up by the time you reach home. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Subject + will have been + V1 + ing + Object | I will have been waiting here for three hours by six o’clock. |
Tag:Comprehensive guide to English tenses, English tense chart, English tense structure explained, Enhance your writing with proper tenses, Essential guide to English verb tenses, Examples of English tenses, Explore different types of tenses, Improve your grammar with tense chart, Learn English tenses easily, Mastering English tenses, Tense, Tense chart for language learners, Tense rules and examples, Tenses in English made simple, Types of tenses explained, Understand English verb tenses